Fig. 6. Ventriculomegalia. Signo del limón
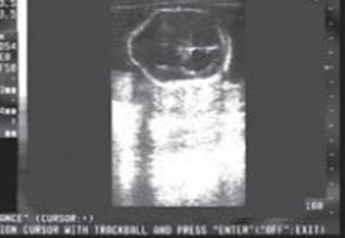
Figura 7. Pie Bot.
Referencias bibliográficas
1. Haslam RH. Malformaciones congénitas del Sistema Nervioso Central. En: Behrman, Kliegman, Arvin. Nelson. Tratado de Pediatría. 15 ed. Madrid: McGraw-Hill; 1998. p. 2085-2088.
2. Chopra S, Manpreet, Gulati S, Shashi Bala P, Hatimota P, Jain R, et al. Spectrum in spinal disraphism. Europ Radiol. 2007; 11:497-505.
3. Sbragia L, Machado IN, Rojas CEB, Zambelli H, Miranda ML, Bianchi MO, et al. Evolução de 58 fetos com mielomeningocele e o potencial de reparo intra-uterino. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2004;62(2-B):487-91. [ Links ].
4. Petzold A, Stiefel D, Copp AJ. Amniotic fluid brain-specific proteins are biomarkers for spinal cord injury in experimental myelomeningocele. J Neurochem. 2005;95(2):594-8. [ Links ].
5. 163ª Asamblea Mundial de la Salud. Ginebra: Organización Mundial de Salud. [consultado 12 Sept 2015]. Disponible en: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/events/2010/wha63/es/.
6. Delgado OL, Lantigua A, Cruz G, Díaz C, Berdasquera D, Rodríguez S. Prevalencia de defectos congénitos en recién nacidos. Rev Cubana Med Gen Integr. 2007; 23(3): 1-4. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0864-21252007000300007.
7. García Y, Fernández RM, Rodríguez M. Incidencia de las malformaciones congénitas mayores en el recién nacido. Rev Cubana Pediatr. 2006; 78 (4). Disponible en: http://www.bvs.sld.cu/revistas/ped/vol78_04_06/ped03406.htm.
8. Goldschmidt EL, Tello AM. Prevención de los defectos del cierre del tubo neural. Revista del Hospital de niños de Buenos Aires. 2000,42: 238-244.
9. Delgado OL, Lantigua A, Cruz G, Díaz C, Berdasquera D, Rodríguez S. Prevalencia de defectos congénitos en recién nacidos. Rev Cubana Med Gen Integr. 2007; 23(3): 1-4. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0864-21252007000300007.
10. García Y, Fernández RM, Rodríguez M. Incidencia de las malformaciones congénitas mayores en el recién nacido. Rev Cubana Pediatr. 2006; 78 (4). Disponible en: http://www.bvs.sld.cu/revistas/ped/vol78_04_06/ped03406.htm.
11. Reduction in Neural-Tube Defects after Folie Acid Forti-fication in Canadam engl j med 357;2 www.nejm.org july 12, 2007.
12. Mc Lone DG. Results of treatment of children born with myelomeningocele. Clin Neurosurg 1983; 30: 407-12.
13. Ames M, Schut L. Diagnosis and treatment: results of treatment of 171 consecutive myelomeningocele, 1963 to 1968. Pediatrics 1972; 50: 466-70.
14. Shields N, Taylor NF, DoddKJ. Self-concept in children with spina bífida compared with typically developing childre. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008 Oct;50(10):733-43
15. Dennis M, Barnes MA. The cognitive phenotype of spina bifida meningomyelocele Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2010; 16(1): 31-9.
16. Obesity across the lifespan among persons with spina bífida. Disabil Rehabil. 2009; 31(11): 914-20.
17. Poley GE and Slater JE Latex allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000;105:1054-1062.
18. Chang CK, Wong TT, Huang BS, Chan RC, Yang TF. Spinal dysraphism: a cross-sectional and retrospective multidisciplinary clínica-based study. J Chin Med Assoc. 2008 Oct;71(10):502-8
19. Hannay HJ, Dennis M, Kramer L, Blaser S, Fletcher JM Partial agenesis of the corpus callosum in spina bifida meningomyelocele and potential compensatory mechanisms. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2009 Feb;31(2) 180-94 .
20. Chang CK, Wong TT, Huang BS, Chan RC, Yang TF. Spinal dysraphism: a cross-sectional and retrospective multidisciplinary clínica-based study. J Chin Med Assoc. 2008 Oct;71(10):502-8
21. Tobias N, Mason D, Luthenhoff M, Stoops M, Ferguson D. Management principles of organic causes of childhood constipations. J Pediatr Health Care. 2008 Jan-Feb; 22(1):12-23.
22. Camargo, Ulloa, Calvo y Lozano: radiología básica básica editorial Celsus, 2001.
23. Filli RA. Evaluación ecográfica del eje neural fetal. En: Ecografía en obstetricia y Ginecología Callen PW (ed) 3ª edición. Buenos Aires: Ed.Médica Panamericana, 1995; 207-55.
24. Henrry, JB: El Laboratorio y el diagnóstico clínico. Editorial Marbàn 2005.
25. Longman C, Mercuri E, Cowan F, et al. (2004). Antenatal and postnatal brain magnetic resonance imaging in mus-cle–eye–brain disease. Arch Neurol 61: 1301–1306.
26. Williams LJ, et al: Prevalenceofspina bifida and anencephalyduringthe transition to mandatory folic acid fortification in the UnitedStates. Teratology 66:33, 2002